Sleep improvement makes cardio training and strength training more effective
Strength training and cardio programs become more effective when trainers not only tell their clients how to train, but they also learn how to sleep better. This information makes athletes slimmer, fitter and perhaps also more muscular and stronger. This is evident from an experimental study that American exercise scientist Brett Dolezal, affiliated with the David Geffen School of Medicine, published in Sports Medicine International Open.
Study
The researchers got 34 healthy men and women aged 22-44 to train for 12 weeks in a gym. The test subjects trained 3 times a week. Each workout consisted of a cardio part and a strength training part.
For 19 test subjects it remained the same, but 14 test subjects viewed an interactive presentation for 10 minutes per week in which they were given information about the importance of sleep and ways to improve their sleep.
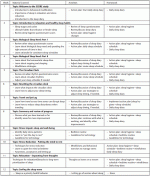
The figure below gives you an impression of what information the test subjects received. Click on the figure for a larger version.
Results
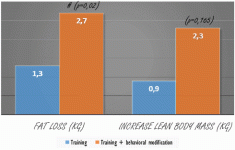
The subjects who received information about sleep lost significantly more body fat than the subjects in the other group. There was also a trend that the sleep information increased the increase in muscle mass, but this increase was not statistically significant.
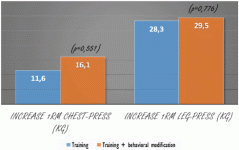
There was also a trend that sleep information increased the increase in muscle strength. However, the difference between the two groups that you see below was not statistically significant.
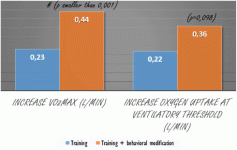
The subjects who combined training with a program that should improve sleep became fitter than the subjects who only trained. And this difference between the groups was statistically significant.
Conclusion
"This study demonstrates that a novel, multicomponent behavioral modification intervention delivered by fitness professionals with the goal of optimizing fitness outcomes was more efficacious atimproving various measures of aerobic performance, [and] body composition, [...] compared with identical exercise training with an equal-attention control", the researchers summarize.
"Our findings indicate not only that sleep interventions have the potential to directly enhance physical performance and autonomic cardiac regulation, but that these interventions can be successfully administered by trained fitness professionals in a non-medical setting."
"Future investigations should explore the replicability and utility of these results in special populations such as elite athletes and those afflicted with lifestyle diseases."
Source: Sports Med Int Open. 2019 Jul 15;3(2):E48-E57.
Strength training and cardio programs become more effective when trainers not only tell their clients how to train, but they also learn how to sleep better. This information makes athletes slimmer, fitter and perhaps also more muscular and stronger. This is evident from an experimental study that American exercise scientist Brett Dolezal, affiliated with the David Geffen School of Medicine, published in Sports Medicine International Open.
Study
The researchers got 34 healthy men and women aged 22-44 to train for 12 weeks in a gym. The test subjects trained 3 times a week. Each workout consisted of a cardio part and a strength training part.
For 19 test subjects it remained the same, but 14 test subjects viewed an interactive presentation for 10 minutes per week in which they were given information about the importance of sleep and ways to improve their sleep.
The figure below gives you an impression of what information the test subjects received. Click on the figure for a larger version.
Results
The subjects who received information about sleep lost significantly more body fat than the subjects in the other group. There was also a trend that the sleep information increased the increase in muscle mass, but this increase was not statistically significant.
There was also a trend that sleep information increased the increase in muscle strength. However, the difference between the two groups that you see below was not statistically significant.
The subjects who combined training with a program that should improve sleep became fitter than the subjects who only trained. And this difference between the groups was statistically significant.
Conclusion
"This study demonstrates that a novel, multicomponent behavioral modification intervention delivered by fitness professionals with the goal of optimizing fitness outcomes was more efficacious atimproving various measures of aerobic performance, [and] body composition, [...] compared with identical exercise training with an equal-attention control", the researchers summarize.
"Our findings indicate not only that sleep interventions have the potential to directly enhance physical performance and autonomic cardiac regulation, but that these interventions can be successfully administered by trained fitness professionals in a non-medical setting."
"Future investigations should explore the replicability and utility of these results in special populations such as elite athletes and those afflicted with lifestyle diseases."
Source: Sports Med Int Open. 2019 Jul 15;3(2):E48-E57.