Hormone factor in Royal Jelly keeps skin young
Hormonal factors play a role in skin aging. The skin of post-menopausal women can age more rapidly due to the rapid decrease in the concentration of estradiol in the blood. Supplementation with Royal Jelly may offer hope, Korean researchers suggest on the basis of an animal study they conducted.Royal Jelly, a hormonal lubricant
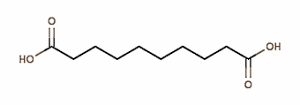
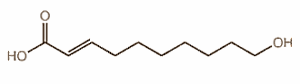
Royal Jelly has an effect on hormones. Exactly how this works is not known, but the active substances are probably fatty acids such as sebacic acid [the first structural formula shown below], 3.10-dihydroxydecanoic acid and above all 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid [second structural formula shown below].[FONT="]
[/FONT]
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
The fatty acids in Royal Jelly work as a kind of hormonal lubricant. According to a 2010 study published in PloS, the fatty acids change the way in which estradiol interacts with its receptor. [PLoS One. 2010 Dec 22;5(12):e15594.] It may just be that the same fatty acids can do the same to receptors for other hormones – such as the androgen receptor.
Study
In 2011 the Koreans published the results of a test-tube study in which Royal Jelly delayed skin aging as a result of exposure to UV light. [J Med Food. 2011 Sep;14(9):899-906.] In that study Royal Jelly stimulated the production of collagen in skin cells.
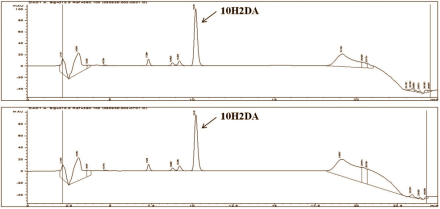
The animal study referred to here was published a year later and builds on the Koreans' first publication. They gave female rats, in which they had halted the production of estradiol, food containing 10 g/kg fresh Royal Jelly. The researchers used two types of Royal Jelly: one from Pocheon [OP] and one from Cheorwon [OC] in Korea. Analyses showed that in both products 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid [10H2DA] was the fatty acid present in the highest quantities.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
Two other groups of rats were given food that contained no Royal Jelly. One group was still capable of producing estradiol [SHAM], the other not [OVX].Results
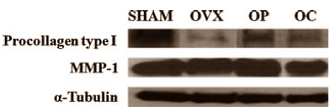
The researchers observed that supplementation prevented a decrease in the amount of protein and collagen in the skin as a result of lower estradiol levels. And this was because the Royal Jelly enabled the rats to continue producing pro-collagen type-1 despite the absence of estradiol.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
When the Koreans searched the literature for other studies in which the fatty acids in Royal Jelly boost the production of collagen, they came across in-vitro studies carried out in Japan. [Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2004 Apr;68(4):767-73.] The research there shows that 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid stimulates collagen production by getting cells to manufacture more transforming growth factor-beta 1 [TGF-beta-1].
Human dosage
Going by the dose that the Koreans used for their rats, a rough estimate for an adult human would be 6-8 g Royal Jelly per day.
The researchers were financed by the Korean government – and not by the supplements industry.
Source:
J Med Food. 2012 Jun;15(6):568-75.

|
[/FONT]


[FONT="]
[/FONT]
The fatty acids in Royal Jelly work as a kind of hormonal lubricant. According to a 2010 study published in PloS, the fatty acids change the way in which estradiol interacts with its receptor. [PLoS One. 2010 Dec 22;5(12):e15594.] It may just be that the same fatty acids can do the same to receptors for other hormones – such as the androgen receptor.
Study
In 2011 the Koreans published the results of a test-tube study in which Royal Jelly delayed skin aging as a result of exposure to UV light. [J Med Food. 2011 Sep;14(9):899-906.] In that study Royal Jelly stimulated the production of collagen in skin cells.
The animal study referred to here was published a year later and builds on the Koreans' first publication. They gave female rats, in which they had halted the production of estradiol, food containing 10 g/kg fresh Royal Jelly. The researchers used two types of Royal Jelly: one from Pocheon [OP] and one from Cheorwon [OC] in Korea. Analyses showed that in both products 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid [10H2DA] was the fatty acid present in the highest quantities.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]

[FONT="]
[/FONT]
The researchers observed that supplementation prevented a decrease in the amount of protein and collagen in the skin as a result of lower estradiol levels. And this was because the Royal Jelly enabled the rats to continue producing pro-collagen type-1 despite the absence of estradiol.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]

[FONT="]
[/FONT]
When the Koreans searched the literature for other studies in which the fatty acids in Royal Jelly boost the production of collagen, they came across in-vitro studies carried out in Japan. [Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2004 Apr;68(4):767-73.] The research there shows that 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid stimulates collagen production by getting cells to manufacture more transforming growth factor-beta 1 [TGF-beta-1].
Human dosage
Going by the dose that the Koreans used for their rats, a rough estimate for an adult human would be 6-8 g Royal Jelly per day.
The researchers were financed by the Korean government – and not by the supplements industry.
Source:
J Med Food. 2012 Jun;15(6):568-75.
