In vitro study: ashwagandha inhibits Alzheimer's
There's nothing wrong with your brains, at least not yet, but you're worried about developing Alzheimer's or dementia. Or perhaps you're one of the lucky ones who've already contracted it, but you're not about to go down without putting up a fight. Molecular scientists at Newcastle University have a suggestion. The Indian herb ashwagandha - scientific name Withania somnifera - inhibits the formation of beta-amyloid plaques. At least, it does so in test tubes.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
Alzheimer's
Amyloid beta consists of 40-42 amino acids. It accumulates in the brains of people suffering from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, but how this happens we don't know. Preventive and complementary approaches to combating Alzheimer's focus on small plant-based molecules, such as curcumin, rosmarinic acid, tannic acid, catechins and quercetin.
These plant substances are thought to prevent the amyloid-beta peptides from clumping together to form plaques in the brain. [Chem Biol Drug Des. 2006 Jan; 67(1): 27-37.] Brain cells are capable of breaking off loose peptides, but not plaques.
Amyloid-beta is toxic for brain cells. In 2010 the researchers published the results of a test-tube study which showed that ashwagandha extracts reduce its toxicity for brain cells. [Phytother Res. 2010 Oct; 24(10): 1567-74.]Study
In a more recent study, which has been published in Phytotherapy Research, the researchers looked at whether water-based ashwagandha extracts also inhibit clumping of beta-amyloid peptides. They were inspired by the Ayurvedic tradition, in which doctors have been using ashwagandha for centuries as a remedy for forgetfulness and as a ‘brain booster'.
Results
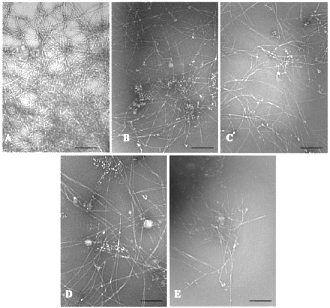
The photos below show how small beta-amyloid fibres formed in the presence of increasing concentrations of ashwagandha extract in the test tubes. A; only peptide amyloid beta (50 microgram per ml); B: Plus 6.25 microg ashwagandha per ml; C: plus 12.5 microg ashwagandha per ml; D: plus 25 microg ashwagandha per ml; E: plus 50 microg ashwagandha per ml.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
 [FONT="]
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
The researchers repeated their experiments with cholesterol in the test tubes. Cholesterol induces clumping of beta-amyloid peptides. [Micron. 2002;33(7-8):609-26.] [Micron. 2008 Dec; 39(8):1192-6.] In this case too ashwagandha extracts inhibited the formation of the fibres.
The researchers are not yet able to say anything about the mechanism behind ashwagandha's ability to inhibit plaque formation and they also emphasise that tests still need to be done on living organisms. Nevertheless they are optimistic.
Conclusion
"The extract of Withania somnifera root could have the potential to become an effective therapy for Alzheimer's Disease patients, as well as a primary or secondary preventive agent for younger healthy individuals and patients with mild cognitive impairment."
Source:
Phytother Res. 2012 Jan;26(1):113-7.
There's nothing wrong with your brains, at least not yet, but you're worried about developing Alzheimer's or dementia. Or perhaps you're one of the lucky ones who've already contracted it, but you're not about to go down without putting up a fight. Molecular scientists at Newcastle University have a suggestion. The Indian herb ashwagandha - scientific name Withania somnifera - inhibits the formation of beta-amyloid plaques. At least, it does so in test tubes.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]

[FONT="]
[/FONT]
Alzheimer's
Amyloid beta consists of 40-42 amino acids. It accumulates in the brains of people suffering from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, but how this happens we don't know. Preventive and complementary approaches to combating Alzheimer's focus on small plant-based molecules, such as curcumin, rosmarinic acid, tannic acid, catechins and quercetin.
These plant substances are thought to prevent the amyloid-beta peptides from clumping together to form plaques in the brain. [Chem Biol Drug Des. 2006 Jan; 67(1): 27-37.] Brain cells are capable of breaking off loose peptides, but not plaques.

|
In a more recent study, which has been published in Phytotherapy Research, the researchers looked at whether water-based ashwagandha extracts also inhibit clumping of beta-amyloid peptides. They were inspired by the Ayurvedic tradition, in which doctors have been using ashwagandha for centuries as a remedy for forgetfulness and as a ‘brain booster'.
Results
The photos below show how small beta-amyloid fibres formed in the presence of increasing concentrations of ashwagandha extract in the test tubes. A; only peptide amyloid beta (50 microgram per ml); B: Plus 6.25 microg ashwagandha per ml; C: plus 12.5 microg ashwagandha per ml; D: plus 25 microg ashwagandha per ml; E: plus 50 microg ashwagandha per ml.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]


[/FONT]
The researchers repeated their experiments with cholesterol in the test tubes. Cholesterol induces clumping of beta-amyloid peptides. [Micron. 2002;33(7-8):609-26.] [Micron. 2008 Dec; 39(8):1192-6.] In this case too ashwagandha extracts inhibited the formation of the fibres.
The researchers are not yet able to say anything about the mechanism behind ashwagandha's ability to inhibit plaque formation and they also emphasise that tests still need to be done on living organisms. Nevertheless they are optimistic.
Conclusion
"The extract of Withania somnifera root could have the potential to become an effective therapy for Alzheimer's Disease patients, as well as a primary or secondary preventive agent for younger healthy individuals and patients with mild cognitive impairment."
Source:
Phytother Res. 2012 Jan;26(1):113-7.
